Finding the user's language in iOS
When localising your app, you might need to get the user’s preferred language, for example for sending it to the backend. There are several ways to do this, let’s have a look at the available APIs Apple provides.
Locale.current
Locale consists of region and language and is mostly used for formatting text such as currency and dates.
The user’s region information is found at the bottom of Settings → General → Language & Region). It is perfectly reasonable to choose another region than the language you’d like the have the phone in. An American living in Norway might like to have the phone language set to American English while using the metric system and a 24-hour clock.
Now, for the language, Locale will find the best match between the languages that your app supports and the user preferred languages. The first language in the preferred list that exists in the app will be chosen.
Locale.preferredLanguages
This returns a list of the user’s preferred languages, in the order they are specified. Note that this list might include more than (or none of) the languages your app supports.
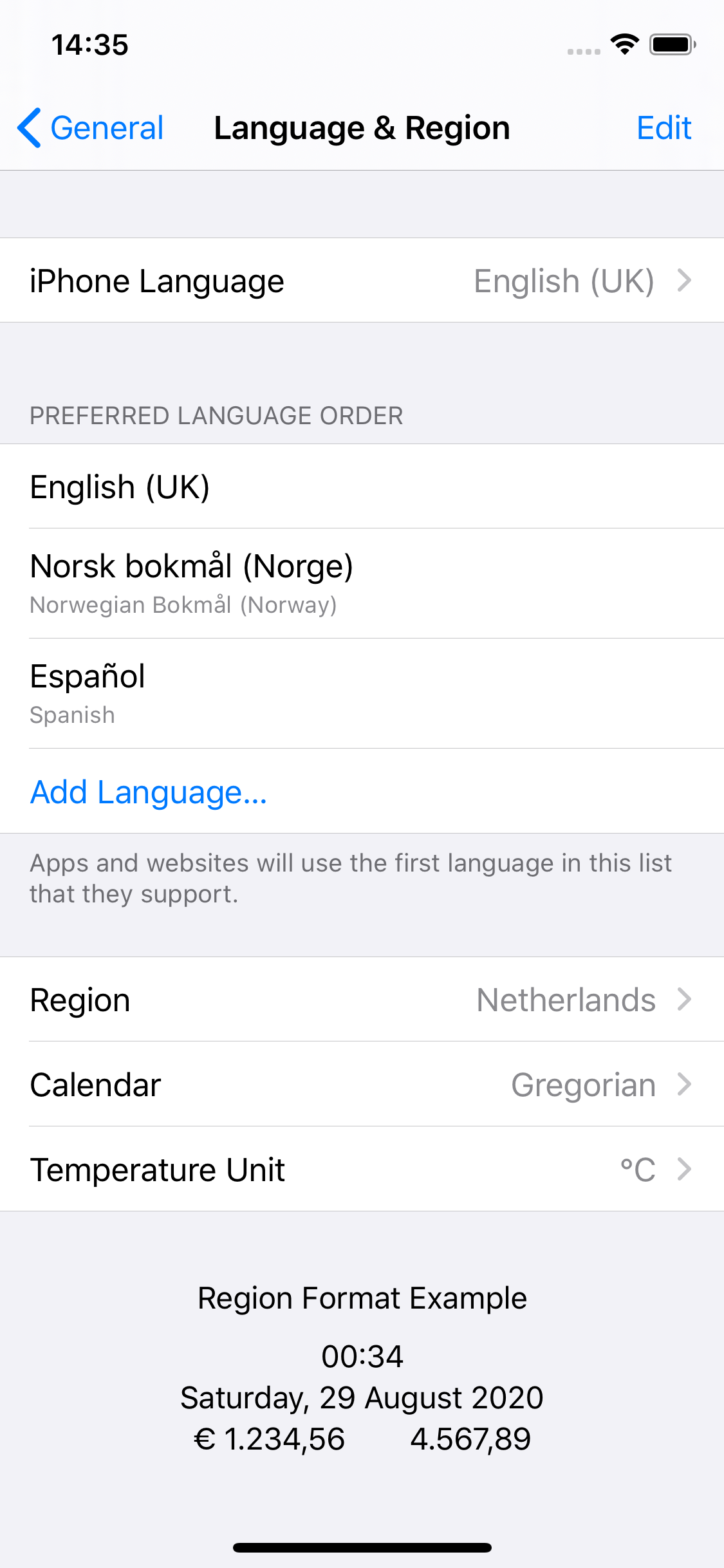
In this example, Locale.preferredLanguages will give ["en-GB", "nb-NO", "es-NL"].
Also note that the user’s preferred language might not be supported by iOS itself, such as Persian:
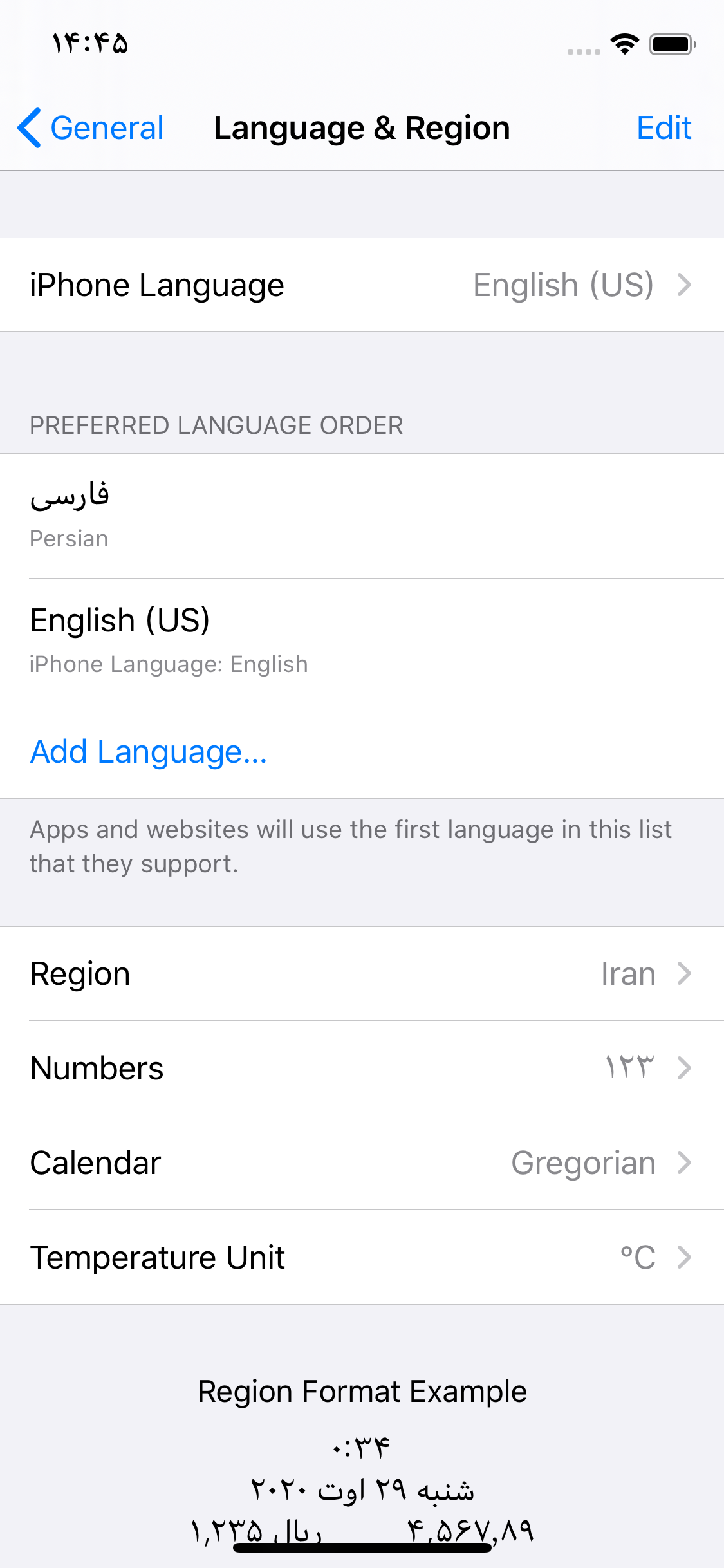
In this case, Locale.preferredLanguages will give ["fa-IR", "en-US"].
Bundle.main.localizations
This will return an array of strings containing all the localisations supported by the app.
Bundle.main.preferredLocalizations
This is a subset of Bundle.main.localizations filtered and sorted according to the user’s preferred languages. This means that Bundle.main.localizations.first will be equal to Locale.current.languageCode.